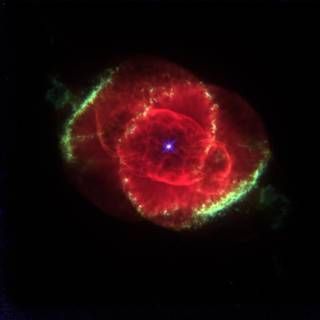
Qur'an - Rosette Nebula
More than 1400 years ago, the Holy Qur'an described the Rosette Nebula in Chapter 55, Verse 37. Traditionally, the verse has been interpreted as the condition of skies at the end of the world. However, we would like to present a couple of other complementary views too.
فَإِذَا ٱنشَقَّتِ ٱلسَّمَآءُ فَكَانَتْ وَرْدَةً كَٱلدِّهَانِ
"And when the heaven is
rent asunder and becomes red rose, like hot melting oil (or dyed leather)" 55:37
1- The first part of the verse "And when the heaven is "rent asunder" may refer to items 4, 5 and 6 in the Summary section above. The fact that the central cavity was not there initially. God caused it to split open at some point in time and that's what gives Rosette the appearance of a rose (mentioned in the 2nd part of the verse)! The interesting fact is that the above action is still being performed. The central cavity of Rosette Nebula is continuously expanding, opening up, and it is getting bigger due to stellar winds and radiation!
"Rent asunder"
may also refer to the following - When a rocket or space shuttle takes off from the Earth and climbs into the space, it moves forward by splitting open the atmosphere. Additionally, using different types of telescopes affords us to gaze into the space and observe things that normally we are not able to see. Therefore, cleaving the sky by a telescope and watching beyond may also match the meaning of the above verse.
2- The second part of the verse describes the red rose in the sky: "becomes red rose" (Summary, item 1 & 2). Also, the verse means that initially it isn't a red rose but later becomes one, similar to the description of the Summary item 5 & 6. Note that scientifically, the central cavity had not been there initially. As it was explained above in the Science section, the cavity has been forming over many light years and without the cavity, it would not look like a rose.
3- The word
كَالدِّهَانِ
in the verse means "hot melting oil" or "dyed tan leather". The Arabic word used highlights "hot" and "melting". Isn't that the Science Summary item 3 above?! The "dyed tan leather" may refer to how this nebula resembles a painting or artwork done on leather (with various shades of paint).
Additional Notes:
The study of kinematic properties, angular momentum and amount of dark matter in the halos of early-type galaxies (ETGs) is limited by the rapid fall-off of the stellar surface brightness. This difficulty can be overcome by using radial velocities of Planetary Nebulae (PNe), which can be obtained much further out than traditional absorption-line kinematics, given their bright emission lines. The Rosette Nebula with scientific name of NGC 2237 is mentioned in verse 37 of Sura Ar-Rahman. Its Radial Velocity is 37.6 czB (where c is the speed of light and zB is the observed relative wavelength shift reduced to the solar-system barycenter, at an epoch equal to the barycentric time of light arrival).
Video courtesy of WindowsofIslam.com
This website frequently incorporates material, pictures, and videos sourced from space explorations, nature, arts, architecture, and scientific achievements. These elements serve as a compelling testament to the intricate and captivating nature of creation. While utilizing selected visuals and videos from external sources under the Fair Use Act, we always strive to acknowledge the origins of these materials. However, it is important to note that their inclusion should not be interpreted as an endorsement of any particular organizations.